
गुरुवार Oct 23 2025 03:34

6 मिनट

Alphabet stocks analysis: Alphabet issues two primary share classes that trade under distinct tickers.
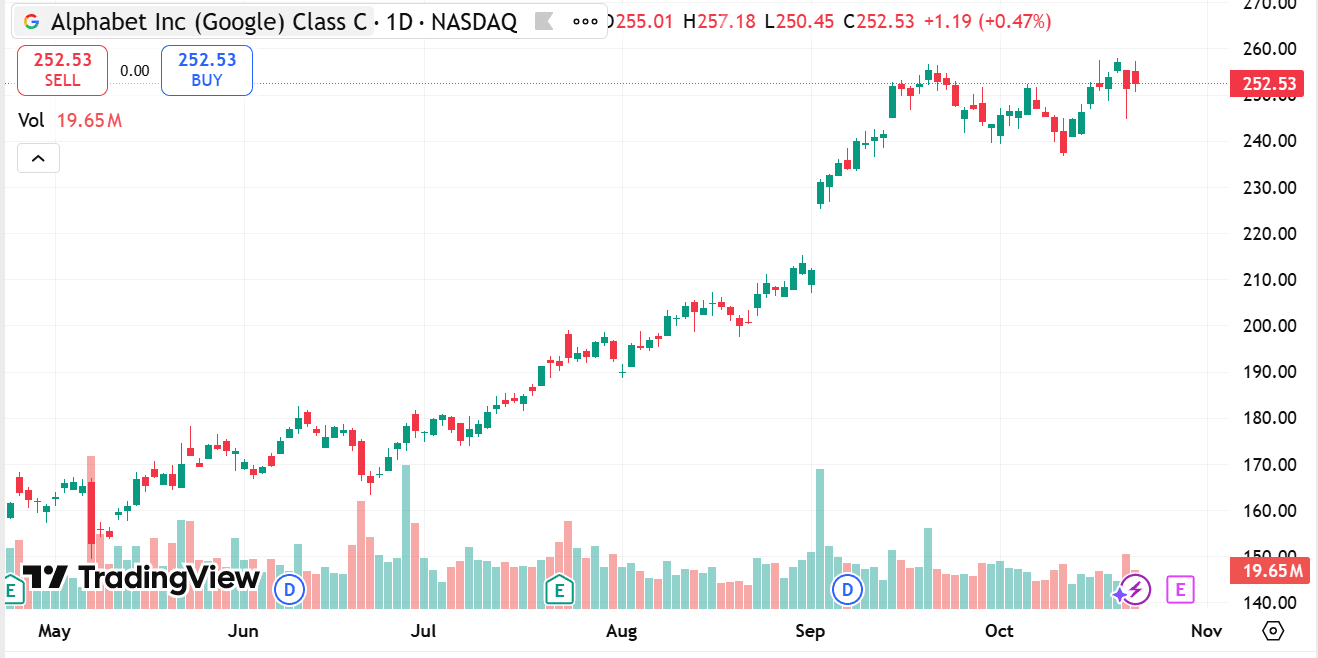
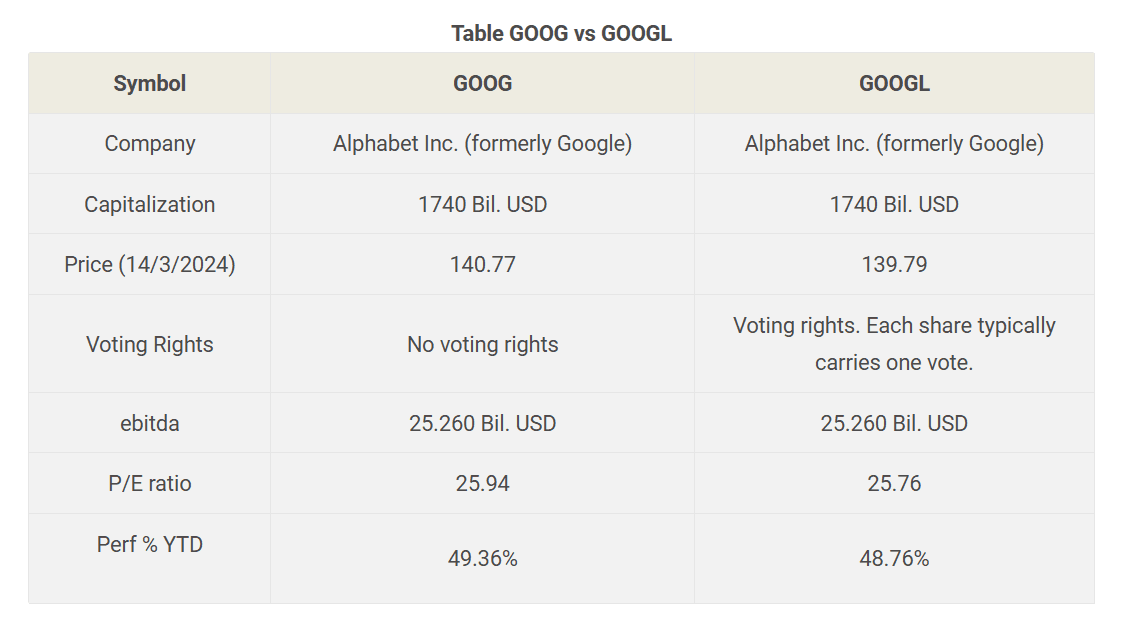
1, GOOG vs GOOGL: Overview
One class carries standard voting rights tied to ownership, while the other class carries enhanced voting power per share. The dual-class structure was created to allow the company’s leadership to retain tighter control over strategic direction while still accessing public capital markets. For holders, the main practical difference is voting influence: one share class gives greater leverage in corporate decisions, the other provides economic exposure without the same level of governance weight. Economically, both classes participate in the company’s earnings and capital moves, and corporate actions such as splits or dividends are typically applied across classes according to established terms.
source: tradingview
2, GOOG vs GOOGL: Price change trend
Price movement between the two share classes generally tracks closely because both represent ownership claims on the same underlying business and cash flows. However, small valuation spreads can appear and persist due to the difference in voting rights, retail versus institutional buying patterns, and liquidity differences across venues. Market participants may bid one class slightly higher or lower at times based on preference for governance influence, tax or account rules, or trading convenience. Over time, these spreads often narrow as arbitrage and active trading exploit price differentials, but temporary deviations can occur around corporate events or periods of uneven demand.
3, How to buy GOOG or GOOGL shares?
Purchasing either class follows the standard process for buying U.S.-listed equities through a brokerage account. Confirm whether your chosen platform supports both tickers and check any account-level restrictions that could affect which class you can trade. Place an order using the ticker symbol for the desired class, selecting an order type and size that fits your execution plan. Be mindful of liquidity and spread: less-liquid classes can exhibit wider spreads and greater slippage, especially during volatile periods. For those using tax-advantaged accounts or custodial structures, verify whether any administrative constraints or fee schedules differ by securities type. If voting rights matter to you, confirm how your brokerage handles proxy voting and record-keeping for the share class you choose.
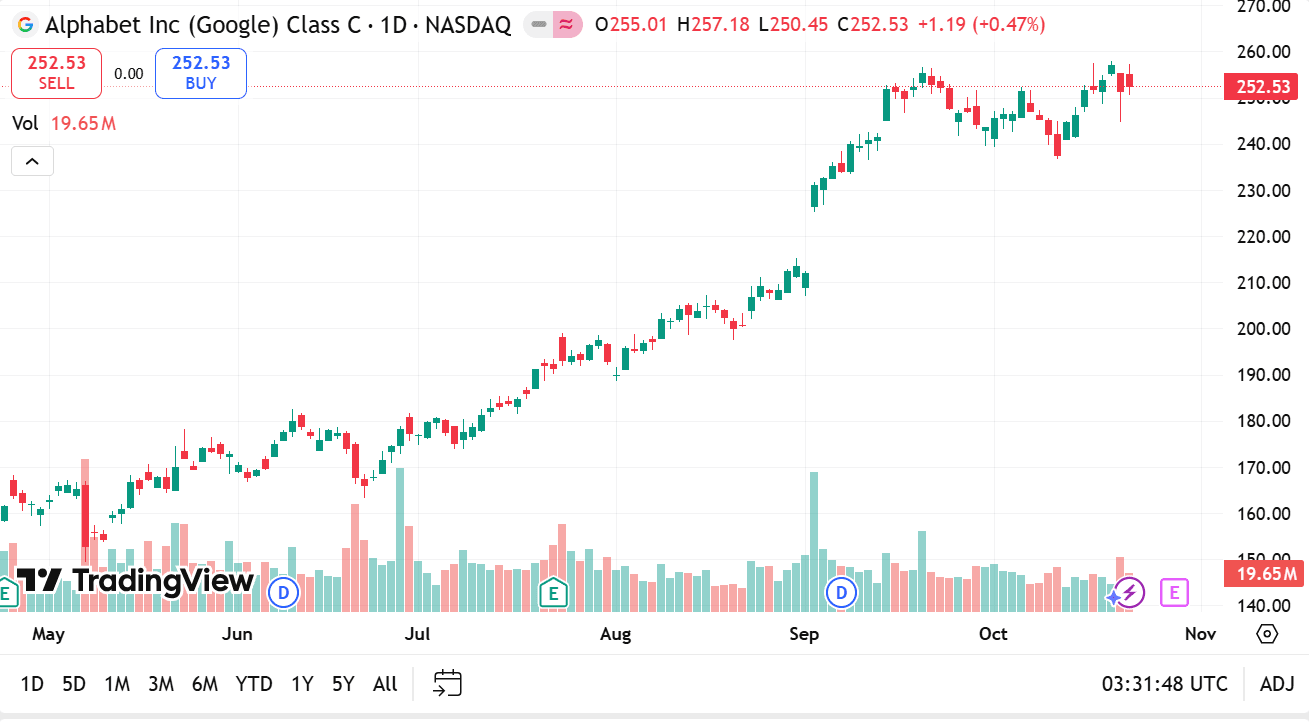
4, GOOG vs GOOGL: Which one should you buy?
The choice hinges on whether voting power matters to your approach. If having a greater formal voice in corporate governance and shareholder votes is important, the class with enhanced voting rights aligns with that preference. If your primary focus is exposure to the company’s business and you place less weight on voting influence, the non-voting or lower-vote class may be perfectly suitable and sometimes offers marginally different liquidity or pricing characteristics.
source: tradingview
Other considerations include tax and account implications, liquidity, and how you expect to trade the holding. For short-term trading, the more liquid class can offer tighter spreads and more reliable execution. For long-term holding, voting rights may matter if you wish to influence corporate direction or be part of shareholder votes on governance items. If you plan to hold through corporate actions, verify how entitlements and record dates apply to each class.
5, FAQs
5.1 What about class B stock?
Class B shares are a separate category historically used by certain founders and insiders to concentrate voting control. They typically carry a multiple of the voting power of publicly traded classes and are often not listed for public trading. In many dual-class setups, Class B shares convert under predetermined conditions, but core holders often maintain this higher-vote stock to preserve strategic control.
5.2 Does having a say in company decisions through voting really matter?
For many holders, voting rights are a governance consideration rather than a day-to-day factor. Shareholder votes cover board composition, executive-compensation frameworks, and major corporate actions. If you care about governance outcomes, corporate direction, or specific policy decisions, higher-vote shares provide a clearer channel to influence those areas. For holders primarily focused on economic exposure and long-term business performance without engagement in governance debates, voting weight may be less important.
5.3 Google Stock Split: Why?
Stock splits are corporate actions intended to adjust the number of outstanding shares while keeping the underlying equity value proportionate. Companies may split shares to make individual share prices more accessible to a broader set of market participants and to improve perceived liquidity. Splits do not change a holder’s proportional ownership or the company’s market capitalisation; they change share count and per-share parings to alter nominal price levels.
5.4 Can traders switch between GOOG and GOOGL?
Yes, traders can purchase either class at will through standard trading mechanisms. However, switching directly between classes is not a single automatic corporate transaction; one must sell one class and buy the other on the open market. Keep in mind the tax ramifications, transaction costs, and potential price spread between the classes when executing such switches. Additionally, market liquidity and timing can affect the cost of moving exposure from one class to another.
5.5 Which is a better long-term investment: GOOG or GOOGL?
For long-term holding, the decision centers on whether you value governance influence alongside economic ownership. If you prefer a formal channel to affect corporate governance and major decisions, the class with greater voting power aligns with that preference. If governance participation is not a priority and you seek exposure to the company’s operating performance with potentially marginally different trading characteristics, the other class may suffice. Both classes reflect claims on the same business fundamentals, so long-term outcomes hinge more on corporate execution, market structure, and industry trends than on which class is held.
Closing thoughts
Both share classes provide exposure to the same core business, but they differ in governance rights and sometimes in trading characteristics such as liquidity and spread. Choose the class that aligns with your priority between governance influence and pure economic exposure, and factor in execution considerations and any account-specific constraints. If you’d like, I can provide a concise pre-trade checklist, a comparison table of the two classes’ typical trading traits, or a walk-through of the buy/sell steps in your chosen brokerage platform.
Risk Warning and Disclaimer: This article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform. Trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs) involves high leverage and significant risks. Before making any trading decisions, we recommend consulting a professional financial advisor to assess your financial situation and risk tolerance. Any trading decisions based on this article are at your own risk.