
What are financial markets: Financial markets play a fundamental role in the global economy by facilitating the exchange of financial assets and enabling participants to manage risk, allocate capital, and access liquidity.
Understanding what financial markets are and how financial trading operates is essential for anyone interested in the world of finance, economics, or personal wealth management. This article explores the nature of financial markets, the key components of financial trading, and the mechanisms that underpin trading activities.
Financial markets are platforms or systems where buyers and sellers come together to trade financial instruments. These instruments include stocks, bonds, currencies, commodities, derivatives, and other assets. The primary function of financial markets is to enable the transfer of funds between those who have surplus capital and those who require capital for various purposes like business expansion, government projects, or personal needs.
Financial markets can be physical locations, such as stock exchanges, or virtual environments facilitated by electronic trading platforms. They operate under rules and regulations that ensure transparency, fairness, and orderly conduct.
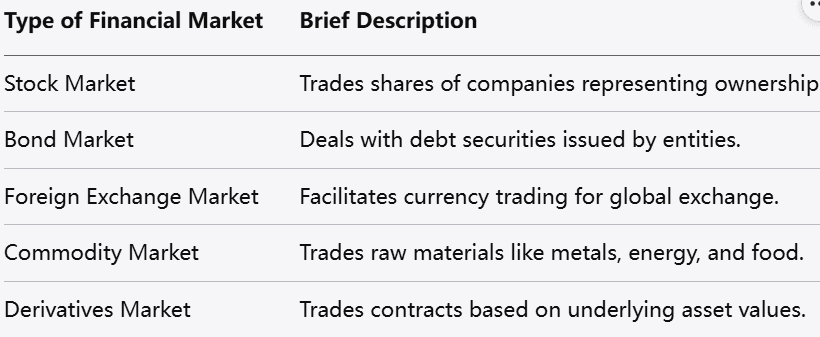
Stock Markets: Where shares of companies are traded, allowing businesses to raise funds and others to participate in ownership.
Bond Markets: Focused on debt instruments issued by governments, corporations, or other entities to borrow money.
Foreign Exchange Markets (Forex): Where currencies are exchanged, supporting international trade and investment.
Commodity Markets: Trading raw materials like oil, gold, agricultural products, which are essential for various industries.
Derivatives Markets: Instruments like futures, options, and swaps that derive their value from underlying assets and are used for hedging or speculation.
Each of these markets serves different functions but collectively contribute to the efficient functioning of the broader economy.
Financial trading refers to the act of buying and selling financial instruments within these markets. Traders seek to exchange assets to manage risk, speculate on price movements, or rebalance portfolios. Trading can occur over various time frames, from seconds (high-frequency trading) to years (long-term holdings).
The Purpose of Financial Trading
Price Discovery: Trading helps establish the price of financial instruments based on supply and demand.
Liquidity Provision: It ensures assets can be bought or sold quickly without causing drastic price changes.
Risk Management: Participants use trading to hedge against adverse price movements.
Capital Allocation: By facilitating exchanges, trading directs resources to their most productive uses.
Financial trading involves a series of steps and participants that interact through the market infrastructure. Here is an overview of the key components and process:
Participants in Financial Trading
Traders: Individuals or entities who buy and sell assets. These include retail traders, institutions, corporations, and governments.
Brokers: Intermediaries that provide access to markets, execute trades on behalf of clients, and offer related services.
Market Makers: Entities that provide liquidity by continuously offering to buy and sell assets at quoted prices.
Exchanges and Trading Platforms: The venues where trades are matched and executed, either physically or electronically.
Trading Process
Order Placement: A trader decides to buy or sell a financial instrument and places an order through a broker or trading platform.
Order Routing: The order is sent to an exchange or market maker for execution.
Order Matching: The market matches buy and sell orders based on price and time priority.
Trade Execution: Once matched, the trade is executed, and ownership of the asset changes hands.
Settlement: The actual transfer of the asset and payment occurs according to market rules and timelines.
Market Orders: Executed immediately at the best available price.
Limit Orders: Executed only at a specified price or better, providing price control.
Stop Orders: Trigger a market or limit order once a preset price level is reached, often used for risk control.
Factors Influencing Financial Trading
Trading activity and asset prices are influenced by a wide array of factors, including:
Economic Indicators: Data on employment, inflation, growth, and other economic measures impact market sentiment.
Monetary Policy: Actions by central banks affect interest rates and liquidity.
Corporate Performance: Company earnings, management decisions, and strategic moves affect stock prices.
Geopolitical Events: Political stability, conflicts, and policy changes can influence markets globally.
Market Sentiment: The collective mood and behavior of market participants impact trading dynamics.
Technological Advances: Innovations in trading platforms and algorithms shape how trading is conducted.

Financial trading inherently involves balancing potential gains against possible losses. Traders employ various strategies to manage this balance, such as diversification, hedging, and position sizing. Understanding risk tolerance and establishing clear trading plans help maintain discipline and avoid emotional decision-making.
Day Trading: Buying and selling within a single day to capitalize on short-term price movements.
Swing Trading: Holding positions for several days or weeks to benefit from medium-term trends.
Position Trading: Long-term approach based on fundamental analysis and broader market trends.

Technology and Financial Trading
Advancements in technology have transformed financial trading. Electronic trading platforms provide real-time data, advanced order types, and access to global markets from anywhere. Automated trading systems use algorithms to execute trades at speeds beyond human capabilities.
This evolution has increased market accessibility and efficiency but also introduced new challenges such as system risks and market volatility.
Regulation and Financial Markets
Financial markets operate under regulatory frameworks designed to protect participants, ensure transparency, and maintain market integrity. Regulations cover aspects like disclosure requirements, trading practices, and capital adequacy of intermediaries.
While regulatory environments vary by country, they share the common goal of fostering trust and stability in financial markets.
Benefits of Financial Markets and Trading
Capital Formation: Markets facilitate funding for businesses and governments, supporting economic growth.
Wealth Management: Trading allows individuals and institutions to grow and manage their wealth.
Price Transparency: Open markets provide clear pricing signals for assets.
Economic Indicator: Market performance often reflects the health of the broader economy.
Financial markets and trading form the backbone of modern economic systems by enabling the efficient exchange of financial assets. Trading is the mechanism through which prices are discovered, liquidity is provided, and risks are managed. Understanding the structure, participants, and processes involved offers valuable insight into how global finance operates.
By navigating financial markets with knowledge and discipline, market participants can engage effectively whether for hedging, portfolio management, or other financial activities. The continuous evolution of technology and regulation ensures that financial trading remains dynamic and integral to economic growth worldwide.
Risk Warning: this article represents only the author’s views and is for reference only. It does not constitute investment advice or financial guidance, nor does it represent the stance of the Markets.com platform.When considering shares, indices, forex (foreign exchange) and commodities for trading and price predictions, remember that trading CFDs involves a significant degree of risk and could result in capital loss.Past performance is not indicative of any future results. This information is provided for informative purposes only and should not be construed to be investment advice. Trading cryptocurrency CFDs and spread bets is restricted for all UK retail clients.